When working on the command line, you are always inside a directory. If you want to list the contents of a directory, you need to use the dir command or ls command. The dir differs from ls in the format of listing contents that is in default listing options. By default, dir command lists the files and folders in columns, sorted vertically and special characters are represented by backslash escape sequences.
Dir Command Description
List information about the FILEs (the current directory by default). Sort entries alphabetically if none of -cftuvSUX nor –sort is speci‐ fied.
Syntax and Options
-a, --all
do not ignore entries starting with .
-A, --almost-all
do not list implied . and ..
--author
with -l, print the author of each file
-b, --escape
print C-style escapes for nongraphic characters
--block-size=SIZE
with -l, scale sizes by SIZE when printing them; e.g.,
'--block-size=M'; see SIZE format below
-B, --ignore-backups
do not list implied entries ending with ~
-c with -lt: sort by, and show, ctime (time of last modification of
file status information); with -l: show ctime and sort by name;
otherwise: sort by ctime, newest first
-C list entries by columns
--color[=WHEN]
colorize the output; WHEN can be 'always' (default if omitted),
'auto', or 'never'; more info below
-d, --directory
list directories themselves, not their contents
-D, --dired
generate output designed for Emacs' dired mode
-f do not sort, enable -aU, disable -ls --color
-F, --classify
append indicator (one of */=>@|) to entries
--file-type
likewise, except do not append '*'
--format=WORD
across -x, commas -m, horizontal -x, long -l, single-column -1,
verbose -l, vertical -C
--full-time
like -l --time-style=full-iso
-g like -l, but do not list owner
--group-directories-first
group directories before files;
can be augmented with a --sort option, but any use of
--sort=none (-U) disables grouping
-G, --no-group
in a long listing, don't print group names
-h, --human-readable
with -l and -s, print sizes like 1K 234M 2G etc.
--si likewise, but use powers of 1000 not 1024
-H, --dereference-command-line
follow symbolic links listed on the command line
--dereference-command-line-symlink-to-dir
follow each command line symbolic link
that points to a directory
--hide=PATTERN
do not list implied entries matching shell PATTERN (overridden
by -a or -A)
--hyperlink[=WHEN]
hyperlink file names; WHEN can be 'always' (default if omitted),
'auto', or 'never'
--indicator-style=WORD
append indicator with style WORD to entry names: none (default),
slash (-p), file-type (--file-type), classify (-F)
-i, --inode
print the index number of each file
-I, --ignore=PATTERN
do not list implied entries matching shell PATTERN
-k, --kibibytes
default to 1024-byte blocks for disk usage; used only with -s
and per directory totals
-l use a long listing format
-L, --dereference
when showing file information for a symbolic link, show informa‐
tion for the file the link references rather than for the link
itself
-m fill width with a comma separated list of entries
-n, --numeric-uid-gid
like -l, but list numeric user and group IDs
-N, --literal
print entry names without quoting
-o like -l, but do not list group information
-p, --indicator-style=slash
append / indicator to directories
-q, --hide-control-chars
print ? instead of nongraphic characters
--show-control-chars
show nongraphic characters as-is (the default, unless program is
'ls' and output is a terminal)
-Q, --quote-name
enclose entry names in double quotes
--quoting-style=WORD
use quoting style WORD for entry names: literal, locale, shell,
shell-always, shell-escape, shell-escape-always, c, escape
(overrides QUOTING_STYLE environment variable)
-r, --reverse
reverse order while sorting
-R, --recursive
list subdirectories recursively
-s, --size
print the allocated size of each file, in blocks
-S sort by file size, largest first
--sort=WORD
sort by WORD instead of name: none (-U), size (-S), time (-t),
version (-v), extension (-X)
--time=WORD
with -l, show time as WORD instead of default modification time:
atime or access or use (-u); ctime or status (-c); also use
specified time as sort key if --sort=time (newest first)
--time-style=TIME_STYLE
time/date format with -l; see TIME_STYLE below
-t sort by modification time, newest first
-T, --tabsize=COLS
assume tab stops at each COLS instead of 8
-u with -lt: sort by, and show, access time; with -l: show access
time and sort by name; otherwise: sort by access time, newest
first
-U do not sort; list entries in directory order
-v natural sort of (version) numbers within text
-w, --width=COLS
set output width to COLS. 0 means no limit
-x list entries by lines instead of by columns
-X sort alphabetically by entry extension
-Z, --context
print any security context of each file
-1 list one file per line. Avoid '\n' with -q or -b
--help display this help and exit
--version
output version information and exitExamples
The basic usage is simple as executing the dir and the output produced may be sufficient in most cases.
dir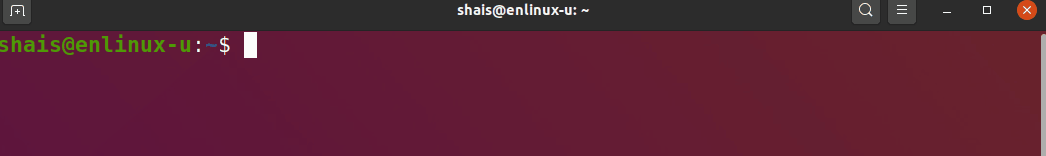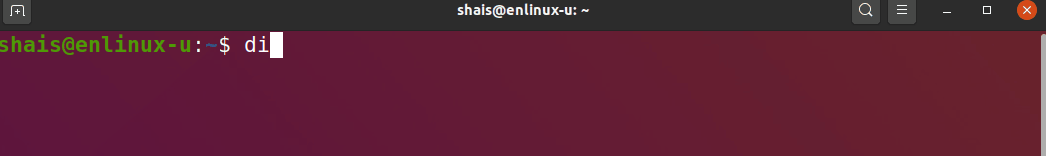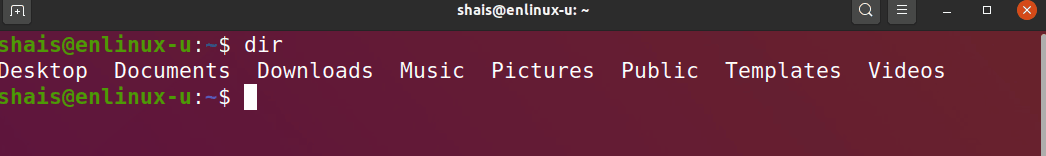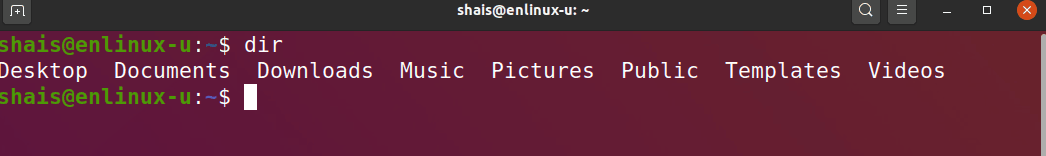
List hidden files with dir command
In case you want to list the hidden files and directories, use the -a command line option.
dir -a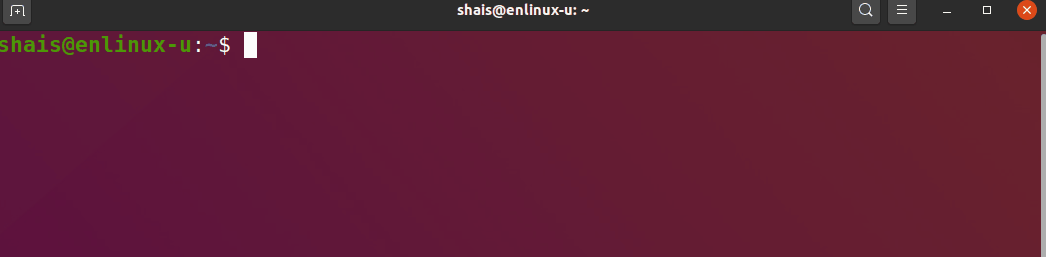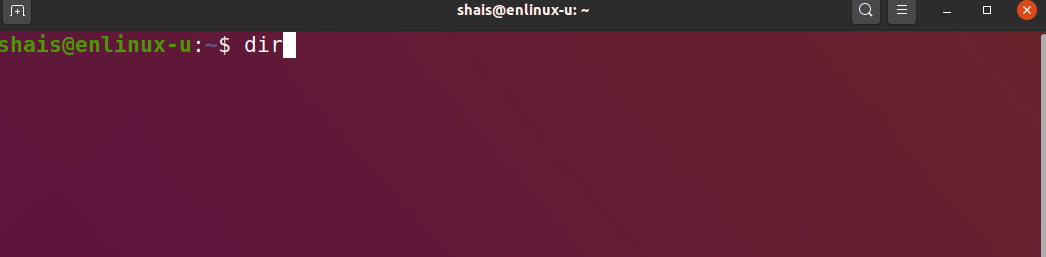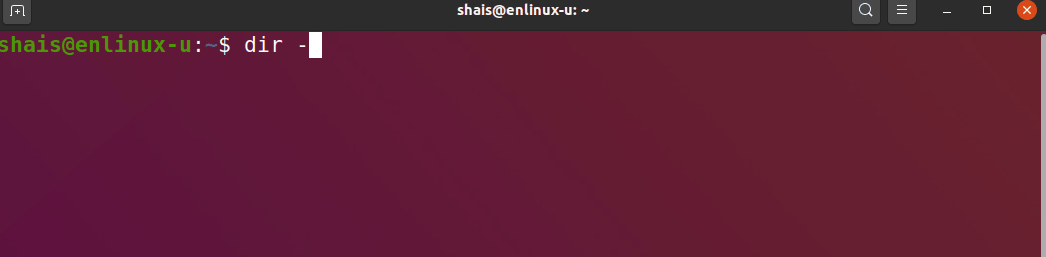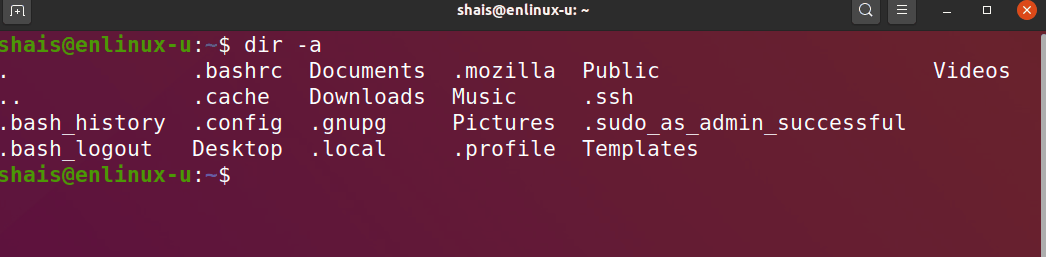
Differentiate between files and directories
dir -F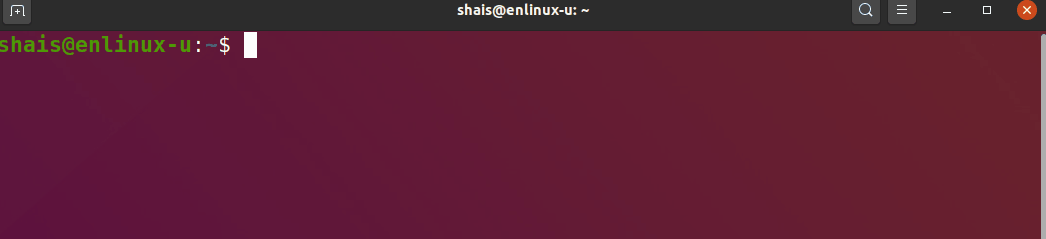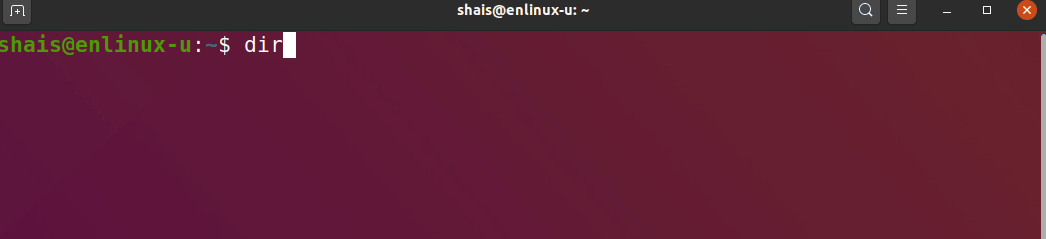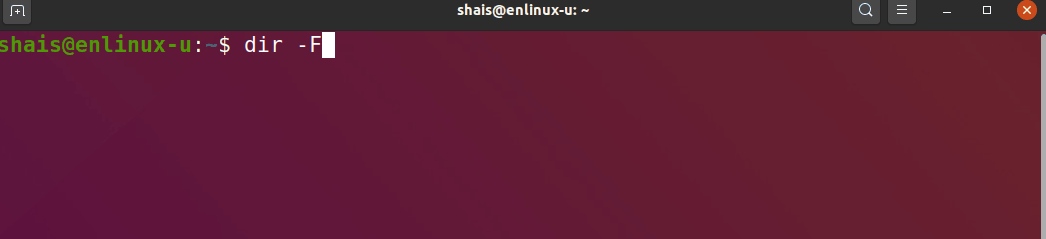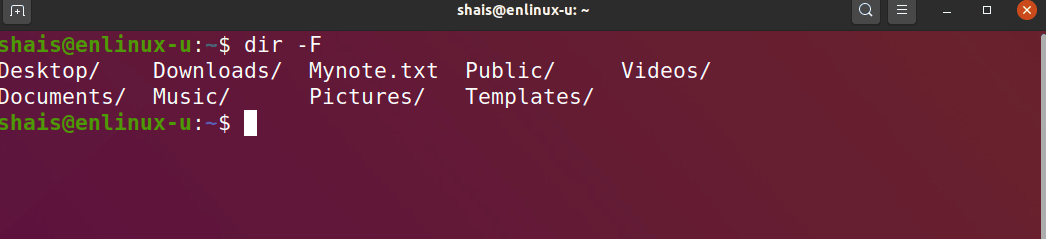
Print out detailed information
dir -L 
More examples:
List detailed information and display the size of directories and fires as human readable format.
dir -lh Sort output by size of file
dir -SReverse and recursively sorted output
dir -rRSEE ALSO
Full documentation at: https://www.gnu.org/software/coreutils/dir
or available locally via: info ‘(coreutils) dir invocation’
This is just an essential guide to dir in all Linux operating system which is working the same in Windows operating system. To learn more and get expert in Linux command line, check command line section and search the name of command you are looking.
